This content is associated with a legacy version of the Replicated product. For the current Replicated product docs, click here.
About the Provisioning API
The Provisioning API enables application developers to expose a set of API endpoints, which Replicated will sync to from the LDAP server.
In this model, applications will have a list of all user accounts, without the passwords. Use the Identity API to authenticate a user in the application.
Replicated brokers the interaction between the identity server and your application. Depending on the identity server used and it’s configuration, changes are propagated to Replicated via push or periodic polling. Applications do not need to have any knowledge of the LDAP server or the LDAP protocol.
If an application indicates it isn’t ready to receive requests by providing anything other than a 2xx response to API calls, the sync will pause and attempt another sync later. Replicated manages a cookie internally to ensure that all messages are delivered.
To use this API, configure the identity field when packaging your application, as documented in the Identity Configuration.
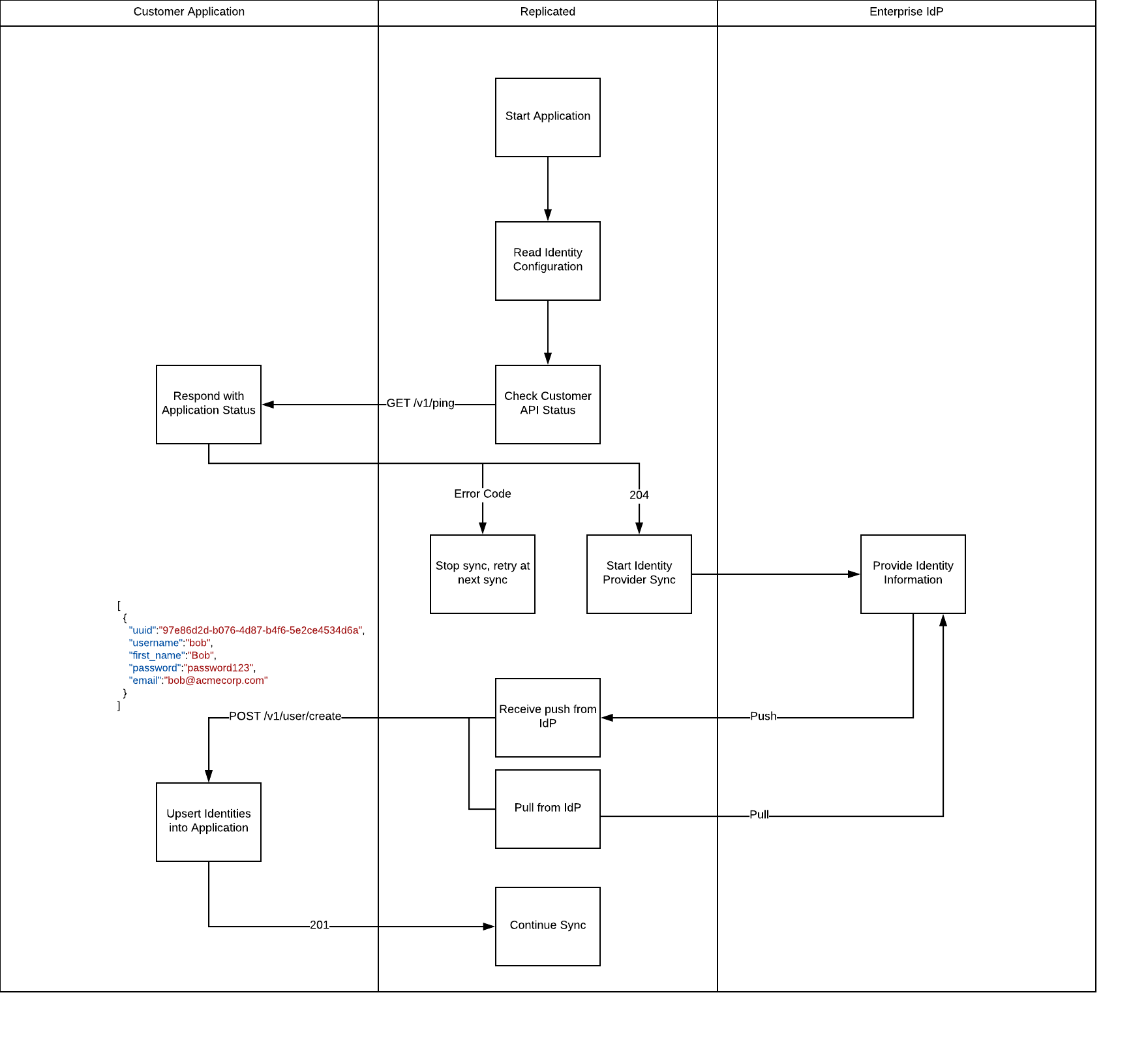
API Flow
When using the Provisioning API, Replicated will bootstrap your user database via an initial sync. After that, it will continue to update your application based on changes. Depending on the identity server used, this can be pull or push on the Replicated side. The Provisioning API will always push user updates to your application.
Initial Sync
During the initial sync phase, Replicated will retrieve all of the available user identities for a given domain search. This will be converted to JSON and posted to the identity endpoint declared in the release YAML identity configuration.
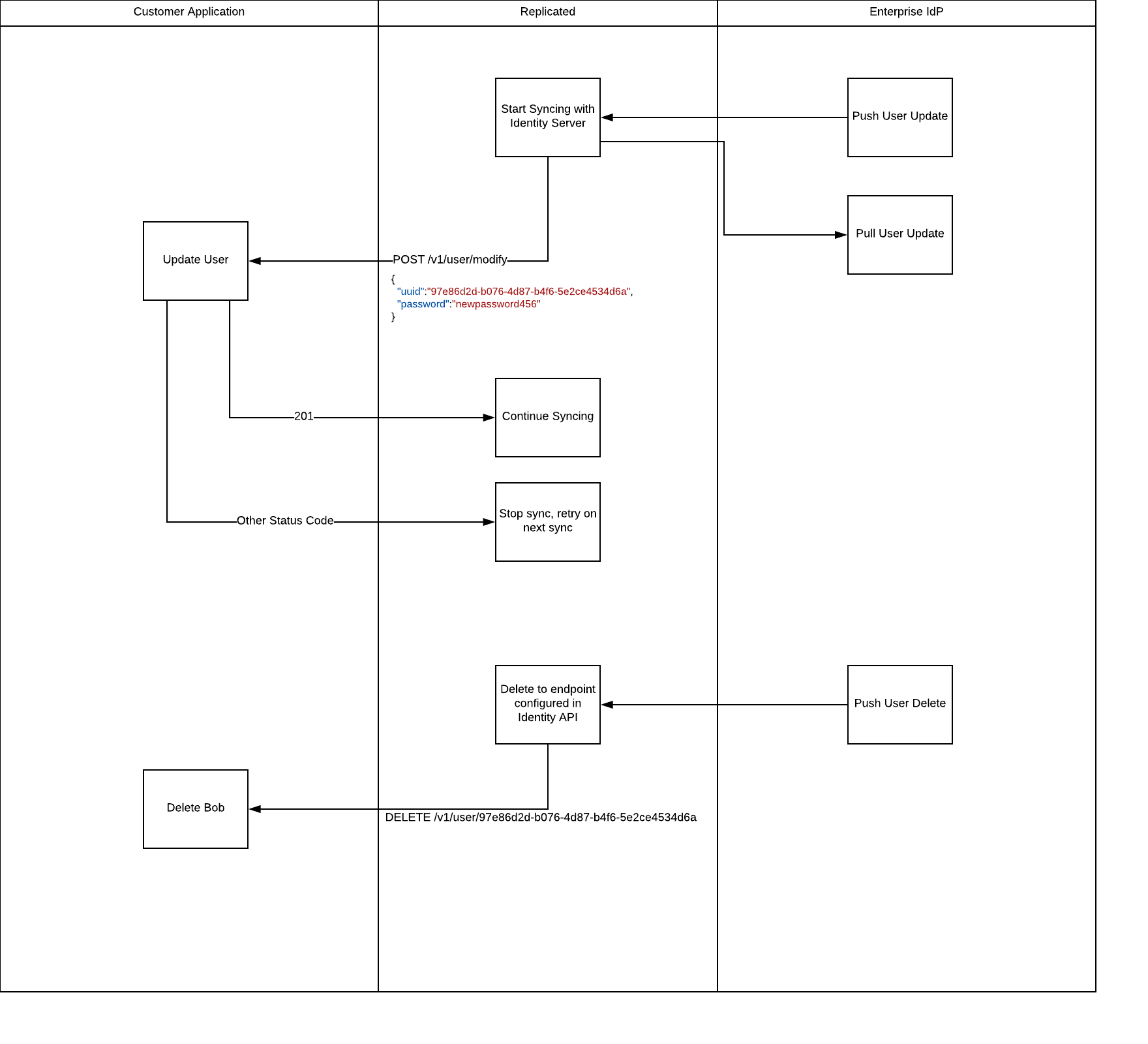
Update Sync
When a user in the identity service is created or changes after the initial sync, Replicated will propgate those changes to the application individually. Applications are responsible for tracking these updates.
If an update fails, syncing will be temporarily stopped. This process will be attempted again during the next sync cycle.
API Methods
GET /v1/ping
This call is used to advertise the API’s readiness.
Response
HTTP status on success: 204
All other status codes will be interpreted as errors and sync will not be initiated.
POST /v1/user/create
This endpoint is called during the initial sync and when a new user record is being created in the LDAP server. The implementation needs to handle duplicate create calls for the same entity gracefully. For example, a record can be updated or the call can be ignored. Returning an error will result in sync being halted.
Request Payload
| Name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| uuid | String | (Required) This is the permanent unique user identifier. Note that username can change but still identify the same user. |
| user_id | String | (Optional) User ID if one is defined by the LDAP server. |
| username | String | (Optional) Username as defined by the ldap_username_field setting. |
| first_name | String | (Optional) First name |
| last_name | String | (Optional) Last name |
| full_name | String | (Optional) Full name |
| password_format | String | (Optional) Password (encryption/hashing) format |
| password | String | (Optional) Password. Note that this maybe clear text password. This will be indicated by the value in password_format |
| String | (Optional) Email |
Response
HTTP status on success: 201
All other status codes will be interpreted as errors and sync will not continue.
POST /v1/user/modify
This endpoint is called when an existing record is being updated in the LDAP server. The implementation needs to handle modify calls for users that don’t exist gracefully. For example, a new record maybe created. However, only uuid is guaranteed to be present in the payload. Returning an error will result in sync being halted.
Request Payload
At this time the request payload is the same as for /v1/user/create
Response
HTTP status on success: 204
All other status codes will be interpreted as errors and sync will not continue.
DELETE /v1/user/:uuid
This endpoint is called when an existing user record is being deleted. Your implementation should return a 204 response on a delete for a user that does not exist.
Request Payload
None
Response
HTTP status on success: 204
All other status codes will be interpreted as errors and sync will not continue.
POST /v1/reset
This endpoint is called when updates to the YAML configuration in the Replicated Admin Console are made by the end-user. This message will be followed by full re-sync from the LDAP server. To enable this feature you must set the identity.enable_reset_request property in your YAML to true. This property is a string and can be templated.
Request Payload
None
Response
HTTP status on success: 204
All other status codes will be interpreted as errors and sync will not continue.